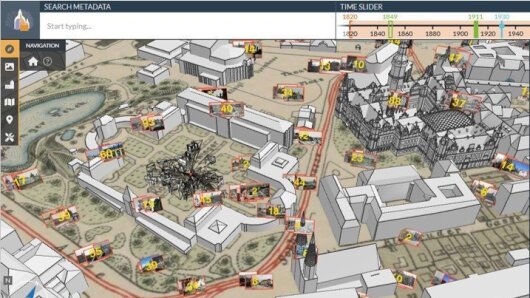
Big data of the late Middel Ages
The cross-faculty MEPHisto research group investigates and develops digital techniques and tools to support historical research.
AI in practice
AI tools and technologies in current research projects